
What are the factors that determine the cutting effect of a metal band saw blade?
personnel
Human factors include operators, engineers and managers. Are the operating procedures for metal band saws reasonable, are the maintenance procedures reasonable and followed, and are band saw operators trained and qualified? Are you cost-conscious and have relevant knowledge and skills? “Personnel” is the most important factor in whether a metal band saw blade can be used well.
The number of saw teeth participating in cutting at the same time
For the application of metal band saw blades, the 3-tooth and 24-tooth principles are usually adopted, that is, the number of teeth involved in cutting at the same time is no less than 3 and no more than 24. Too few teeth will cause tooth pulling, while too many teeth will result in insufficient chip removal from the tooth grooves, unable to cut or bevel cutting or even tooth pulling. In the picture below, the number of teeth involved in cutting is 6 teeth.
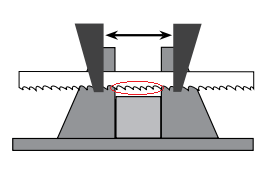
But there are two exceptions, one is cutting with tensile teeth, and the other is cutting large materials with high difficulty (usually up to 48 teeth). How to calculate this? If you are using 3/4 teeth, then the average tooth pitch for this size is 3.5 teeth/inch. If cutting 100mm material, the number of teeth involved in cutting at the same time is about: 3.5*100/25=14 teeth. Here is the key point of correction. The 2/3 teeth and 3/4 teeth we usually refer to refer to metal band saw blades. Tooth pitch, not tooth profile. Tooth profile refers to the shape of one or several teeth combined together. The picture below shows the beveling defect of the workpiece caused by too many teeth.

Tooth profile selection for metal band saw blades
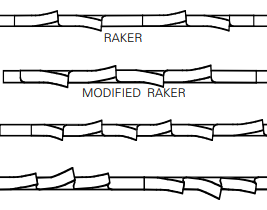
When sawing steel and pipes, tensile teeth are often used. When sawing stainless steel and tool steel, use high and low teeth. When sawing large materials, a certain rake angle is required, otherwise the saw blade will easily lose force. When cutting No. 10 steel, copper, deformed aluminum alloy and other materials, use a metal band saw blade with a large rake angle, which can easily remove chips and provide better surface roughness.
Tooth form selection
Solid materials of 50mm and above require a metal band saw blade with left and right teeth, but for thin-walled pipes, it is actually more reasonable to use a metal band saw blade with corrugated teeth.
Metal band saw speed settings
Different grades of materials, different specifications, different heat treatment states, and different performance of the metal band saw will all affect the speed setting of the metal band saw. The larger the material, the belt speed should be appropriately lowered. For example, for 100mm No. 45 steel, the line speed can be 80m/min, but for 600mm No. 45 steel, the line speed should be set at 50m/min; and for the same 100mm size 304 For stainless steel, the line speed can only be set at 30m/min.
How to visually measure linear speed? If you can see the butt welding joint of the band saw, measure the number of revolutions N it performs in a certain period of time, and the linear speed (m/min) is: L*N/T, (L is the length of the metal band saw blade, the unit is m; T is the time it takes for the band saw to rotate N times, unit is min)
Break-in of new band saw blade
Because the cutting edge of the new band saw blade is too sharp, a break-in process is required when cutting most materials (except titanium and deformed aluminum alloy). The running-in of bi metal band saw blades is generally to reduce the feed speed to half of the normal value, while the running-in of carbide band saw blades is to reduce the linear speed by half (if it is already the lowest, then do not reduce it), and then Adjust the feed to about 1/4 of the normal value and slowly increase it.
Feed rate
If the feed speed of the metal band saw is too fast, it will easily cause skew cutting or tooth pulling, but if the feed speed is too slow (especially materials with a tendency to work harden such as 304 stainless steel), it may also waste the saw blade or cause the metal band saw to break. The operating efficiency is too low.
The quality and stability of metal band saw blades
Every metal band saw blade is different. Every tooth on a band saw blade counts. There are hundreds of knives (edges) on each band saw blade. If only 100 of them are used in cutting, will the overall performance of the metal band saw blade be good? Therefore, it is more reliable to buy saw blades produced by high-quality manufacturers.
Types of Metal Band Saws
There is a big difference in cutting performance between a metal band saw with good rigidity and good maintenance, and a metal band saw with weak rigidity and poor maintenance. If you are cutting difficult materials like high-temperature alloys and the width of the material to be cut is 200mm, it is more reliable to choose a sawing machine with a rated sawing width of 400mm, because the cutting force required for difficult-to-cut materials of the same specifications may be greater than that of ordinary steel. Requires 2 times or even 4 times the cutting force. Therefore, it is necessary to choose a metal band saw with high power to be suitable.
Saw wheels for metal band saws
The parallelism of the two saw wheels must be adjusted properly. The saw wheel cannot be damaged. The bearing clearance in the middle of the saw wheel is normal (does not swing left and right). Ensure that the saw blade is in the middle of the saw wheel and does not swing left or right.

Metal band saw status
New Bandsaw or Old Bandsaw? Is it well maintained? A well-maintained metal band saw will not only extend the life of the band saw, it will also allow a single metal band saw blade to cut more material.
The jaws of a metal band saw should be clamped correctly
Try to keep the jaws clamped as tightly as possible and hold them correctly. If the steel pipes and other materials are clamped in the wrong way, it is easy to cause tooth failure. The following are the correct ways to clamp several materials.

Guide arm for metal band saw
The guide arm determines where the applied feed force is transmitted to the metal band saw blade. The guide arm should be as close to the workpiece as possible and keep the two guide arms on the same plane.
Guide wheels and guide blocks for metal band saws
Damage to the guide wheel will lead to early failure of the saw blade and skewed cuts. Incorrect position of the guide block or incorrect pressure on the pressing block will affect the operation of the metal band saw blade.

Metal band saw brushes
The brush plays the role of removing chips, ensuring that the cutting edge and tooth groove are clean when the metal band saw blade enters the cut again, and can also protect the processed surface of the cut workpiece. If a carbide band saw blade is used, it is recommended to change the brush to a brush with self-powered rotation to increase the cleaning effect, which can extend the life of the saw blade.

Coolant for metal band saws
Coolant cools, lubricates and cleans. It should be adjusted appropriately according to the cutting scene. At the same time, the coolant should be environmentally friendly and efficient, because some coolants are easy to breed microorganisms and affect the health of operators. A concentration of 5% is used for sawing of general materials. When cutting alloy materials with a carbide band saw blade, it is recommended to increase the cutting concentration to 10%. High-speed sawing of non-ferrous metals generally uses minimum quantity lubrication, but attention should be paid to the selection of the grade and type of minimum quantity lubricant.
Hardness of materials suitable for cutting with metal band saws
For bi metal band saw blades, materials above 40HRC are not suitable for processing; for carbide band saw blades, materials above 65HRC are completely unsuitable for processing.
Shapes of materials that metal band saws are not suitable for cutting
Especially thin pipes (such as 0.5mm wall thickness) and particularly small solid materials (such as 10MM) are difficult to process without special fixtures and a good feeding system. Particularly large materials are difficult to process due to the difficulty of applying force to the metal band saw blade.
Is the sawing method a continuous production operation or an intermittent operation?
Intermittent operations do not require so high efficiency and cooling. If you only occasionally cut a 100mm large titanium alloy, there is no need to use a carbide band saw blade, a bimetal band saw blade will suffice.

